No products in the cart.
What is a DDoS Attack?A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack targets websites and servers by disrupting network services. Learn about DDoS attacks and how to prevent them
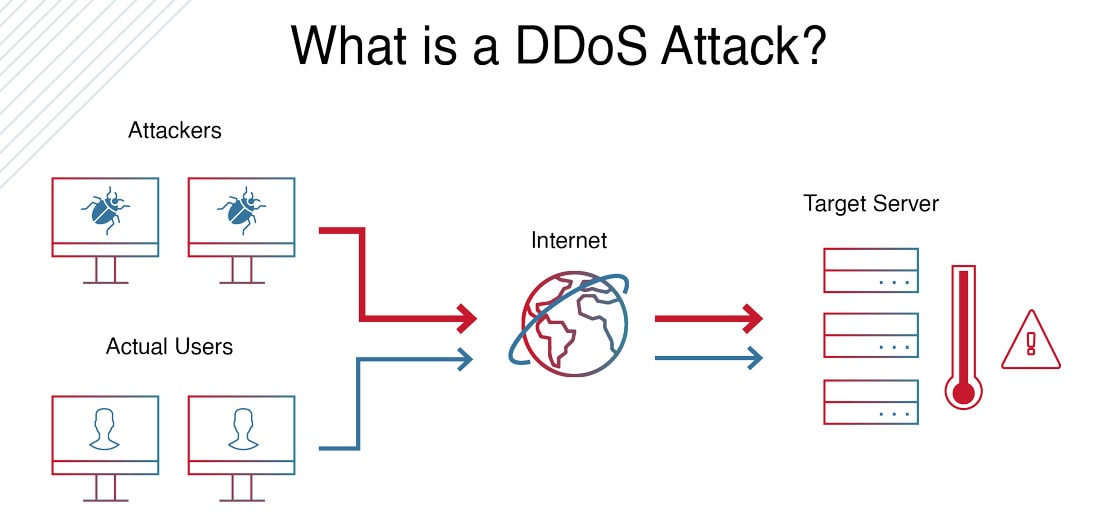
A DDoS attack, meaning a “Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack”, is an attack that occurs when multiple machines are operating together to attack one target to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service, or network, by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic.
DDoS allows for exponentially more requests to be sent to the target, therefore increasing the attack power. It also increases the difficulty of attribution, as the true source of the attack is harder to identify.
DDoS attacks can be devasting to an online business or any type of organization, which is why understanding how they work and how to mitigate them quickly is critical.
The uses of DDoS attacks are very broad, serving as a sharp tool for extortion, disrupting competitors' operations, and even for improving win rates in online games.
In January 2020, Ubisoft Games sued a DDoS attack service provider in the New York area. The provider offered a "room-bombing" service to players, allowing them to launch DDoS attacks on game servers when they were about to lose in a game, causing server lag and rendering the current session invalid.
"Room-bombing" is not a new topic in China either. In 2019, the operating team of Blizzard's game "Overwatch" in China collaborated with law enforcement agencies such as the Shanghai police to crack down on the malicious "room-bombing cheats" in the "Overwatch" game.
In 2017, Tencent's "League of Legends" operating team banned 2189 players for using "room-bombing" programs across all servers.
The objective of a DDoS attack is to deplete the resources of the targeted server, including computing, networking, and storage. By various means, the attacker aims to push the server's computing performance to its limit, fill up network bandwidth, or exhaust storage space, thereby making the server unable to respond to legitimate requests.
According to the OSI seven-layer model, DDoS attacks most commonly occur at the third network layer, fourth transport layer, sixth presentation layer, and seventh application layer.
Third and fourth-layer DDoS attacks are generally referred to as infrastructure layer attacks, usually involving simulating a large number of layer three and four packets like ICMP, UDP, and TCP to prompt server responses, thus depleting server resources.
These attacks are the most common and simplest, with many tools like hping3 available for simulating this DDoS attack. Due to the unique characteristics of this type of attack, developers can more easily identify and take precautions against it.
Sixth and seventh-layer DDoS attacks typically fall under application-layer attacks, whereby attackers simulate application-layer requests such as HTTP to prompt server responses. These attacks are less common than the first type because attackers need to understand how the server-side applications work and construct more complex requests.
Defense measures against DDoS attacks include:
Traffic Analysis: Monitor network traffic and analyze traffic patterns using tools such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems to detect anomalies.
Bandwidth Overprovisioning: Pre-allocate additional bandwidth to network infrastructure to handle potential traffic peaks.
DDoS Mitigation Solutions: Utilize professional DDoS defense services such as Distributed Denial of Service protection offered by cloud platforms.
Hybrid Defense Strategy: Implement a multi-layer defense strategy combining hardware and software to enhance overall security protection.
Response Plan: Prepare a plan to respond to DDoS attacks, including emergency measures and post-attack recovery operations.
Dealing with DDoS attacks requires considering various factors, including technical measures, preventive strategies, and the ability to respond quickly. As attack methods continue to evolve, staying vigilant and updating protective measures is essential.